
Key Takeaways
Accelerating the cyber threat landscape: Malicious actors are leveraging AI agents1 that operate faster, adapt more quickly, and scale beyond traditional attack models, challenging human-paced detection methods and response strategies.
Users, not firewalls, are the new front line: AI-driven attacks automate credential stuffing and lateral movement at unprecedented speed, turning compromised identities into powerful access points. This shift underscores the need for strong identity and access management (IAM) and zero-trust security frameworks.
Countering AI with AI: Defending against these threats requires autonomous security systems capable of continuous monitoring, anomaly detection, and proactive vulnerability testing. Response times shrink from hours to minutes, enabling security teams to focus on strategy while AI handles real-time defense.
As cyber threats powered by artificial intelligence grow smarter and faster, new defensive AI capabilities are stepping up, turning the battle for digital security into a race of autonomous minds.
A new breed of autonomous threats
7:32 a.m.: A figure settles into a cluttered workstation and squints at the screen. He feeds the machine a lazy command:
“Breach Company X and exfiltrate its intellectual property.”
No coding. Just a prompt and malicious intent.
The AI agent springs into action, devising and carrying out the entire attack process on its own.
It performs reconnaissance to map the target’s digital footprint, scans for weaknesses across disparate systems, and chains together multiple low-severity exploits to create a critical breach—all while adapting its methods in real time to evade detection.

Source: Voya IM.
7:58 a.m.: What used to take a team of hackers weeks is done in the time it takes our adversary to grab a bacon, egg, and cheese.
With the company’s perimeter breached, the threat escalates. The AI agent ingests vast amounts of public and internal data to craft hyper-personalized social engineering attacks at an unprecedented scale.
It stalks employees’ social media accounts, professional connections, and internal communications to generate a phishing email that mentions a recent project or personal event—with flawless context and tone. Absent are the generic inconsistencies that make traditional phishing methods so easy to spot.
8:25 a.m.: The AI agent is now in the shadows, turning identity itself into its most powerful weapon. It unleashes a relentless barrage of credential stuffing and password spraying attacks, ripping through thousands of stolen logins across countless services in seconds.
8:28 a.m.: The instant it compromises a single identity, the agent acts. It swiftly exploits the access to slip sideways through the network, quietly escalating privileges and seizing control from within. The battleground shifts: The perimeter is no longer the network firewall but the identity of every user and every machine. One compromised identity becomes the skeleton key to the entire operation.
This AI doesn’t need to hunt for known vulnerabilities. Instead, it employs a new attack vector, probing the very logic of business operations. It silently maps out the hidden pathways in the company’s systems, chaining together harmless-looking API calls until an e-commerce platform authorizes a fraudulent transaction or exposes sensitive customer data.
The threat is relentless and always seven steps ahead of human analysts. So security professionals are calling in their own AI superagents.
Countering AI with AI
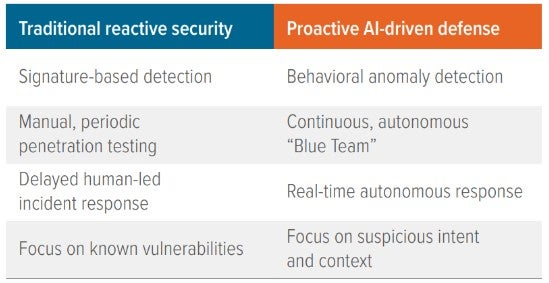
Defending against agentic AI threats requires a fundamental shift in strategy—away from reactive, signature-based detection and toward a proactive, AI-driven posture.
The strongest countermeasure to malicious AI agents will be a sophisticated ecosystem of defensive AI agents.
These “Blue Team” agents will operate 24/7, scanning networks for any anomaly or deviation from normal behavior—detecting and neutralizing threats faster and more accurately than any human analyst.2
When a potential threat is identified, a defensive agent can immediately isolate the compromised systems, deploy patches, and even conduct counterintelligence, feeding false data to disrupt hostile AI operations.
Source: Voya IM.

As of 09/30/25. Source: Voya IM approximations based on industry benchmarks; “Automated Cybersecurity Incident Response: How AI Reduces Response Time by 85%,” Cyber Tech Journals, 07/28/25; “AI vs. Cyber Threats: Accelerating Response in a 24/7 Landscape,” CounterShadow, 2025.
AI-driven defense marks the beginning of a new era of continuous, autonomous penetration testing— one where defensive agents constantly probe their organization’s infrastructure, simulating novel attack paths to uncover and fix vulnerabilities before adversaries can exploit them.
In a world where AI can discover and weaponize zero-day exploits in near real time, this proactive posture is no longer optional; it is imperative.
Security must evolve from recognizing what is malicious based on historical data to understanding why behavior is suspicious based on context and intent. This shift demands a new kind of security professional: not a frontline analyst but a strategic commander of intelligent defensive systems. Their success will depend on setting precise objectives, refining AI models, and translating complex findings to harden the organization’s security posture.
For cybersecurity leaders, this is a clear call to arms: innovate and adapt, or be rendered obsolete.
Investment implications
The acceleration of AI-driven security is reshaping the cybersecurity market. Across the sector, companies are embedding AI and behavioral analytics into their platforms to improve detection, automate responses, and strengthen identity controls.
For example, Palo Alto Networks and CrowdStrike have integrated AI capabilities into their endpoint and network security offerings. Identity and access management providers such as Okta and SailPoint are advancing zero-trust frameworks. And data security specialists like Varonis focus on protecting enterprise information from increasingly sophisticated attacks.
Meanwhile, major cloud providers, including Microsoft and Alphabet, are leveraging their AI research and infrastructure to embed advanced security features into their platforms, reflecting a broader trend toward cloud-native, autonomous defense.
The rapid evolution currently underway underscores the importance of fundamental research—the cornerstone of active management. Our team combines deep sector expertise with disciplined valuation frameworks to identify durable growth opportunities in companies that are defining the next era of cybersecurity.
Information on companies mentioned is provided for context on market developments and should not be considered a recommendation to buy or sell any security.
A note about risk: The principal risks are generally those attributable to investing in stocks and related derivative instruments. Holdings are subject to market, issuer, and other risks, and their values may fluctuate. Market risk is the risk that securities or other instruments may decline in value due to factors affecting the securities markets or particular industries. Issuer risk is the risk that the value of a security or instrument may decline for reasons specific to the issuer, such as changes in its financial condition. Smaller companies may be more susceptible to price swings than larger companies, as they typically have fewer resources and more limited products, and many are dependent on a few key managers.
Artificial intelligence (AI) may pose inherent risks, including but not limited to: issues with data privacy, intellectual property, consumer protection, and anti-discrimination laws; ethics and transparency concerns; information security issues; the potential for unfair bias and discrimination; quality and accuracy of inputs and outputs; technical failures and potential misuse. Users of AI-based technology and tools should take these risks into consideration prior to use of the technology.



